310S is an austenitic alloy comprised of chromium and nickel, renowned for its robust oxidation, corrosion, and high temperature resistance. Boasting a higher percentage of chromium and nickel, this stainless steel offers superior strength and can operate in high temperatures.
| Chemical Composition |
0.05C-25Cr-20Ni |
| Physical Property |
• Density: 7.9 kg/dm³
• Tensile Strength: 600 MPa
• Yield Strenght: 270 Mpa
• Elongation A5: >=35% |
| Stock & Dimensions |
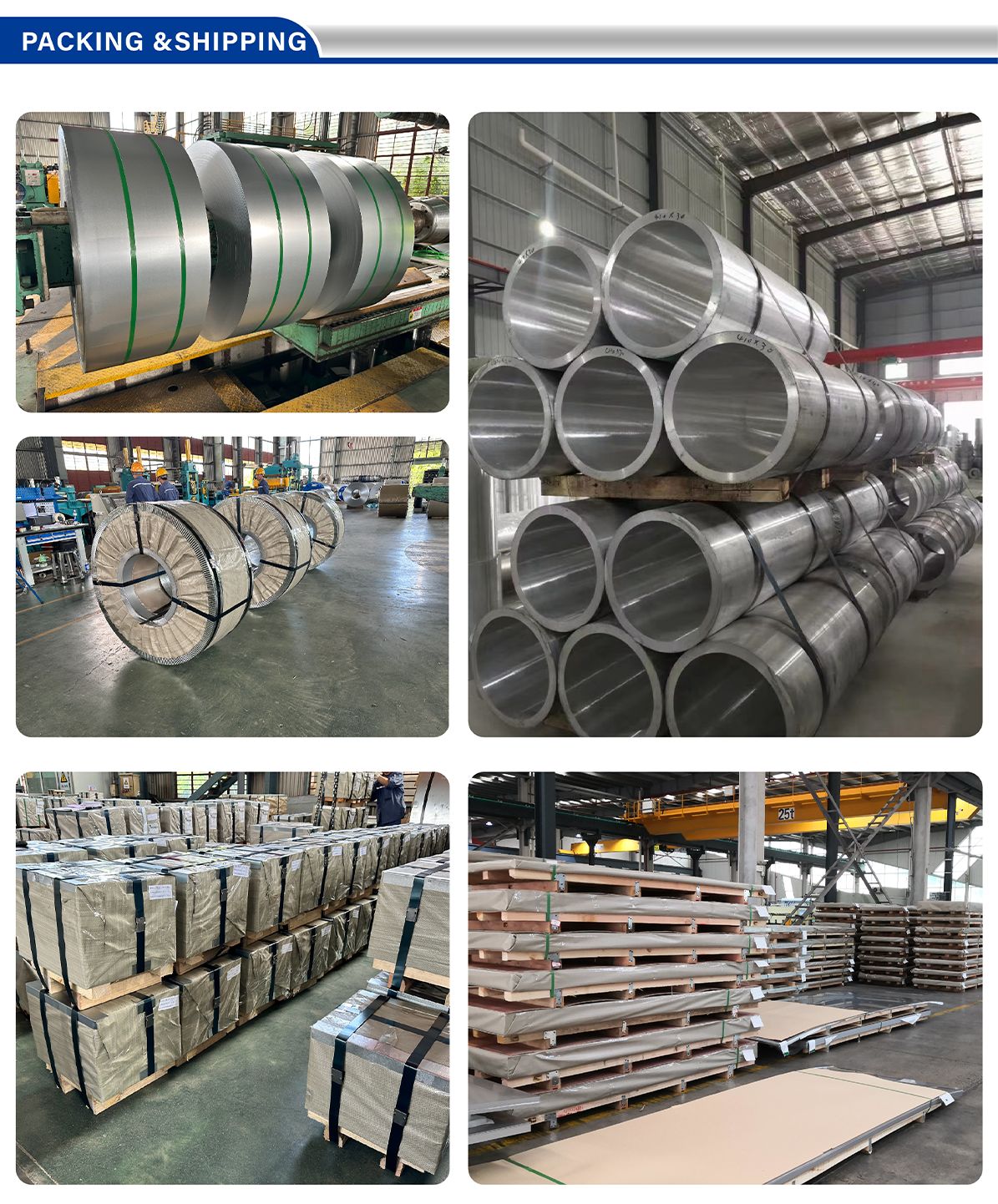
Our warehouse has a large number of stock to provide you with a variety of products in different sizes, and can also customize the size according to your needs.
• Bar: 0.5~600mm Diameter
• Coil: 0.5~150mm Thick
• Plate: 0.5~200mm Thick
• Pipe: 6~630mm External Diameter; 0.5~40mm Wall Tick
• Available in specific sizes |
| Product Forms |
We provide you with a variety of product forms, including but not limited to:
• Bar/Rod
• Pipe/Tube
• Coil/Strip
• Plate/Sheet/Circle
• Wire
• Fitting (Flange, Elbow, Tee...)
• Customize |
Essential details
Grade 310/310S stainless steel (1.4845) is one of the most widely used grades of heat resistant stainless steel supplied into numerous industry sectors.
The key properties of this material are its high chromium and medium nickel content making its resistance to oxidation, sulfidation and other forms of hot corrosion its main characteristics. Whilst retaining good strength when exposed to high temperatures, like most austenitic grades this grade will also maintain its strength and toughness at sub-zero temperatures.
Overall this grade is an excellent choice for various applications ranging from furnace components to burner tips. 310 / 310S has a maximum dry air service temperature of 1100ºC.
Applications:
Used in a number of applications where the temperature exceeds 550°C, e.g. for equipment and components within: industrial furnace equipment, oil industry equipment, heat treatment baskets, heat exchanges, steam boilers and thermo wells, iron, steel, and non-ferrous industries, engineering industry, energy conversion plants, cement industry.









 AISI 444 Stainless Steel | EN 1.4521 Stainless Steel
AISI 444 Stainless Steel | EN 1.4521 Stainless Steel ASTM / AISI 321H / EN 1.4878
ASTM / AISI 321H / EN 1.4878 EN 1.4436 / ASTM 316 Stainless Steel
EN 1.4436 / ASTM 316 Stainless Steel ASTM 304L ( EN 1.4307 ) Stainless Steel
ASTM 304L ( EN 1.4307 ) Stainless Steel ASTM 309S - EN 1.4833
ASTM 309S - EN 1.4833 ASTM 439 - EN 1.4510
ASTM 439 - EN 1.4510 ASTM 434 - EN 1.4113
ASTM 434 - EN 1.4113 ASTM 321 - EN 1.4541
ASTM 321 - EN 1.4541