AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel is meticulously engineered to bolster its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, making it a standout choice for demanding environments. The alloy's composition is characterized by:
Chromium (Cr): Approximately 17.0% to 20.0% , which is the primary element responsible for the steel's outstanding resistance to oxidation and corrosion. Chromium forms a passive layer of chromium oxide on the surface, protecting the metal from further deterioration, especially in chloride environments.
Molybdenum (Mo): Ranging from 1.8% to 2.5% , molybdenum enhances pitting and crevice corrosion resistance, particularly in saline or acidic conditions. This addition significantly improves the alloy's strength at high temperatures and its resistance to chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking.
Titanium (Ti): Around 0.2% titanium acts as a stabilizer , combining with carbon to form titanium carbides. This minimizes chromium carbide precipitation at the grain boundaries during welding, thereby maintaining corrosion resistance in the heat-affected zones.
Carbon (C): Kept at a very low level, generally below 0.025% , to prevent the formation of chromium carbides which could deplete the chromium content at the grain boundaries, reducing the material's corrosion resistance.
Nitrogen (N): up to 0.030% , Controlled addition of nitrogen (up to 0.025%) enhances mechanical strength and corrosion resistance without compromising the material's formability and weldability.
The composition is carefully balanced to ensure optimal performance in corrosive environments, providing a combination of durability, weldability, and high-temperature resistance. This makes AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel particularly suited for applications requiring resilience to both chloride-induced corrosion and high temperatures.
AISI 444 Physical Properties
| Physical Property |
• Density: 7.7 g/cm³
• Electrical resistance: 0.60 μΩ·m
• Thermal conductivity: 23 W/(m·K)
• Specific heat: 460 J/(kg·K)
• Young's modulus: 220 GPa
• 0.2% Yield stress: 275 MPa, min |
| Stock & Dimensions |
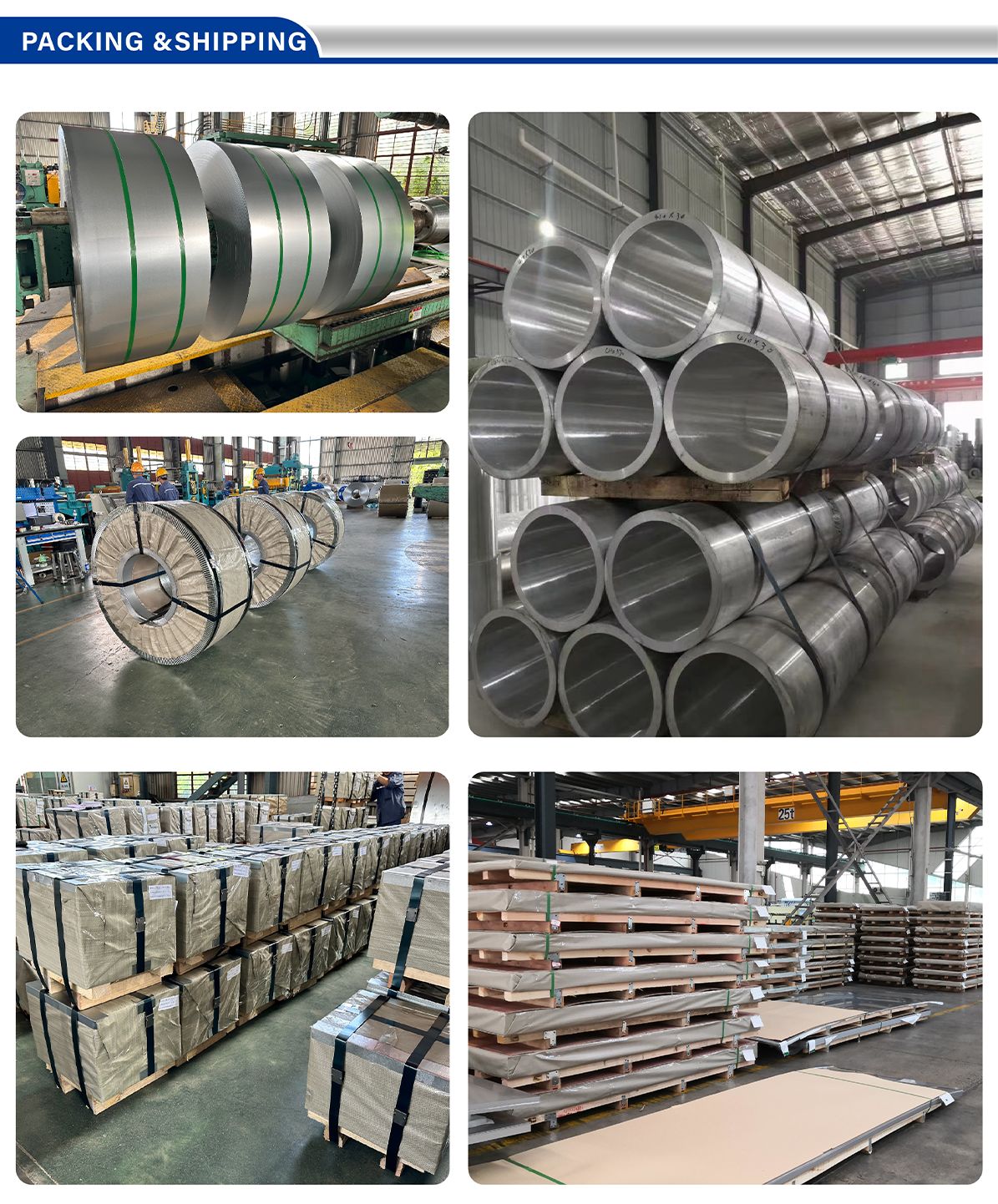
Our warehouse has a large number of stock to provide you with a variety of products in different sizes, and can also customize the size according to your needs.
• Bar: 0.5~600mm Diameter
• Coil: 0.5~150mm Thick
• Plate: 0.5~200mm Thick
• Pipe: 6~630mm External Diameter; 0.5~40mm Wall Tick
• Available in specific sizes |
| Product Forms |
We provide you with a variety of product forms, including but not limited to:
• Bar/Rod
• Pipe/Tube
• Coil/Strip
• Plate/Sheet/Circle
• Wire
• Fitting (Flange, Elbow, Tee...)
• Customize |
AISI 444 vs 316: A Comparison
AISI 444, a ferritic stainless steel, is recognized for its excellent corrosion resistance in chloride-rich environments, making it ideal for marine and water treatment applications. It benefits from a high chromium and molybdenum content, enhancing its pitting and crevice corrosion resistance.
AISI 316, an austenitic stainless steel, contains nickel and more molybdenum, offering broad corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength, suitable for the food and pharmaceutical industries.
The choice between AISI 444 and 316 depends on the application's environmental conditions and mechanical requirements, with AISI 444 excelling in chloride resistance and AISI 316 in versatility and toughness.
| Property |
AISI 444 |
AISI 316 |
| Category |
Ferritic Stainless Steel |
Austenitic Stainless Steel |
| Main Alloying Elements |
High Chromium, Molybdenum |
Nickel, Higher Molybdenum |
| Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent in Chloride Environments |
Excellent Overall, including Acids |
| Applications |
Water Treatment, Marine |
Food Processing, Pharmaceuticals |
| Thermal Expansion & Conductivity |
Lower Expansion, Better Conductivity |
Higher Expansion |
| Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance |
Superior in Chloride Environments |
Good, but less than AISI 444 |
| Toughness & Weldability |
Good, with proper methods |
Excellent, including at Cryogenic Temperatures |
Welding and Fabrication
The AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel is engineered for optimal weldability and fabrication, making it a versatile material for various industrial applications. Here is a detailed overview of its welding and fabrication properties:
Weldability
This grade exhibits excellent weldability using most common welding techniques, attributed to its balanced chemical composition and ferritic microstructure. The presence of chromium and molybdenum enhances its weldability, while the low carbon content minimizes the risk of carbide precipitation during welding, preserving the corrosion resistance of the weld zone.
Recommended Welding Methods
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding: Highly recommended for its ability to produce high-quality, precise welds, especially in thinner materials. TIG welding offers the advantage of controlled heat input, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of AISI 444 / EN 1.4521.
Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding: Suitable for thicker sections due to its faster welding speed. MIG welding is versatile and efficient, making it a popular choice for fabricating AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel structures.
Resistance Welding: This method is effective for joining thin or medium-thick materials, offering high-speed welding with minimal distortion. Its suitability for AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stems from the alloy's excellent electrical conductivity and heat resistance.
Post-weld Heat Treatment
Generally, post-weld heat treatment is not required for AISI 444 / EN 1.4521, thanks to its stable ferritic structure and low carbon content. However, annealing after welding can further enhance corrosion resistance, especially in critical applications. Annealing should be performed at temperatures around 790°C to 815°C (1454°F to 1499°F) followed by rapid cooling to maximize corrosion resistance.
Machinability
AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 offers good machinability when using appropriate tooling and processes, despite being a ferritic stainless steel, which are typically more challenging to machine than their austenitic counterparts. The use of modern cutting tools and techniques can significantly improve machining efficiency. Optimizing cutting speeds, feeds, and the use of suitable lubricants can help in achieving smooth finishes and extending tool life.
In summary, AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel is characterized by its excellent weldability with common techniques, minimal need for post-weld heat treatment, and good machinability, making it a preferred material for a wide range of fabrication projects. Proper welding methods and conditions can ensure the integrity and corrosion resistance of the welded joints, highlighting the alloy's adaptability in various applications.
AISI 444 Applications:
| # |
Application |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Considerations |
| 1 |
Water Treatment and Distribution |
High corrosion resistance in chlorides, durable, reduces maintenance. |
Higher initial cost but offset by longevity. |
Monitor for corrosion in highly chlorinated water. |
| 2 |
Architectural Applications |
Aesthetic appeal, high corrosion resistance, suitable for exteriors in coastal areas. |
Requires proper installation to avoid water trapping. |
Choose appropriate finishes and maintain properly. |
| 3 |
Automotive Components |
Resists corrosion and high temperatures, ideal for exhausts and trim. |
Potential for galvanic corrosion in mixed-material assemblies. |
Ensure welding/fabrication processes maintain material properties. |
| 4 |
Chloride-rich Environments |
Excellent at resisting pitting and crevice corrosion, ideal for marine settings. |
May require frequent inspections in aggressive environments. |
Implement corrosion management strategies. |
(FAQ) About AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel

1.What is AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 Stainless Steel and its primary benefits?
AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel is a high-chromium, molybdenum-alloyed, nickel-free ferritic stainless steel known for its excellent corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich environments. Its primary benefits include superior resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, high-temperature performance, and excellent weldability. This makes it ideal for applications in water treatment and distribution, architectural structures, automotive components, and environments exposed to corrosive elements. Its cost-effectiveness and durability make it a preferred choice for many industrial applications.
2.What maintenance and care are required for AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 Stainless Steel to ensure its longevity?
To ensure the longevity of AISI 444 / EN 1.4521 stainless steel, regular maintenance and care are essential. This includes routine cleaning to remove contaminants that may cause corrosion, such as salts, chlorides, and acidic substances. It's also important to inspect the material periodically for signs of wear or corrosion, especially in critical applications and harsh environments. Avoiding contact with incompatible metals can prevent galvanic corrosion. If welding or fabrication is performed, following best practices and proper cleaning post-processing will help maintain the material's corrosion resistance and structural integrity.
Customer Reviews for XFT AISI 444 / EN 1.4521
-
1.Michaela Quinn
★★★★★
"Our clients have been extremely satisfied with the durability and aesthetic appeal of this material."
-
2.Eduardo Rivera
★★★★★
"It has drastically improved the longevity and reliability of our systems"
-
3.Sophie Beaumont
★★★★★
"Its resistance to chloride-induced corrosion has extended the life of our products, providing great value to our customers."











 ASTM / AISI 321H / EN 1.4878
ASTM / AISI 321H / EN 1.4878 EN 1.4436 / ASTM 316 Stainless Steel
EN 1.4436 / ASTM 316 Stainless Steel ASTM 304L ( EN 1.4307 ) Stainless Steel
ASTM 304L ( EN 1.4307 ) Stainless Steel ASTM 310S - EN 1.4845
ASTM 310S - EN 1.4845 ASTM 309S - EN 1.4833
ASTM 309S - EN 1.4833 ASTM 439 - EN 1.4510
ASTM 439 - EN 1.4510 ASTM 434 - EN 1.4113
ASTM 434 - EN 1.4113 ASTM 321 - EN 1.4541
ASTM 321 - EN 1.4541